Posts Tagged ‘Leadership’
Looking Back, Looking Ahead: Lessons learned and what’s to come in 2018-2019
As consultants, our role is to guide our partners to make informed decisions and to successfully meet their goals. We also prioritize building the knowledge and skills of our partners and they tell us that they learn a lot from working alongside us. In turn, we learn so much every day from the incredibly smart and diverse partners we have the good fortune to work with!
As we reflect on the past and look ahead to the new school year, we are grateful for all that we have learned from our clients. In our next couple of blog posts, each Hendy team member will share something he or she has learned and something we’re excited about it. It’s going to be a great year!
To kick us off, read below from our founder, Sarah Rosskamm:
What I learned: Change is hard. Often times the solution is to prepare for change, engage stakeholders, continuously communicate the “why”, work with influencers, plan for challenges and ultimately to just keep going even when it gets tough. There are times, however, when the solution is to pause, reflect and change course. In working with one of our partner charter networks this year, we learned that sometimes the most courageous and best answer is to stop doing something. In this case, our partner was eager to build a teacher career pathway. They took many important steps to get there, had buy-in from leaders and momentum from teachers believing it was valuable. However, they also had budget changes, shifts in capacity and new demands of their attention. As a result, they smartly decided to pause. They stopped putting their attention into the pathway and instead narrowed the scope of their focus to implementing a highly effective evaluation and development structure that would help their teachers to grow and enable them to target their professional learning activities. They focused on laying a foundation that would immediately benefit teachers through continued growth, and will ultimately allow them to move more quickly toward a pathway if and when they choose to pick it up again. It wasn’t easy (for the network or for the Hendy team) to not complete our original shared goal, but it was the right thing to do for their teachers and students.
What I’m excited about: Hendy Avenue’s very first consulting project was supporting the Delaware Department of Education as they considered revisions to their teacher evaluation rubric. After considering several rubric options based on the best of the available rubrics at the time, the Delaware team, similar to the team described above, decided to pause and learn more before making changes to a statewide tool. So, we shifted course and supported four charter schools in Wilmington to design and implement an alternative evaluation system for their teachers that would utilize this new rubric. I worked closely with the leaders in those schools for several years and together we instituted an alternative system that is now used in a growing number of Delaware schools through their Alternative Evaluation system. I am so excited that five years later, after learning a great deal about the use of the current rubric and about the alternative system, Delaware leadership is eagerly partnering with teachers, leaders and other stakeholders to revise the rubric to ensure the tool is well-aligned to new standards and meets the needs of teachers across the state. I’m also thrilled the state has very wisely decided to prioritize involvement of teachers and leaders in the process and to take the time necessary to ensure it’s a positive and welcomed change for their well deserving teachers. And I’m even more excited that Hendy Avenue will be partners in engaging stakeholders, designing, piloting, revising and ultimately building a rubric that helps teachers and leaders be the very best they can be for their students.
Making Teacher Leadership a Success
In our first post on teacher leadership, we noted a few key ideas and benefits of extending the impact of teachers. Here, we break down three suggestions for launching a new teacher leadership initiative as well as criteria to measure success and common pitfalls to avoid.
How do you launch a successful teacher leadership program?
Our research and experience suggest three critical steps to starting a new approach to teacher leadership:
- Start with a goal in mind: Avoid launching a new program without a clearly defined, and important problem to solve. For example, if your district finds that teachers are not feeling valued in decision making, a teacher leadership program aimed at increasing teacher voice would be more appropriate than a peer coaching initiative.
- Identify the right “strand” of teacher leadership: Teacher leadership can be instructional (coaching, learning communities, etc.), associative (organizing, community building, etc.) or policy focused (advocacy, implementation feedback, etc.).
- Build a leader profile and plan for their development: Identify the specific knowledge, skills, and mindsets teacher leaders will need to be successful. Consider the personal or professional goals teacher leaders could be working towards and how they’ll be held accountable to meeting the expectations for their role.
Criteria for Success
Successful implementation of any initiative requires specific benchmarks in order to direct action, mobilize energy and inspire persistence. At the same time, setting goals is not enough. In addition to guidance, training and coaching, people need the capacity to act.
Here are four criteria that leaders can use to achieve success:
- Alignment: Ensure teacher leadership priorities are aligned with overall school priorities.
- Goals: Collaboratively set and track progress against clear, measurable goals for teacher leadership.
- Systems of Support: Identify a clear, cohesive system of support for teacher leaders to drive their professional growth and success.
- Schedules: Carefully plan and agree upon scheduling to guarantee teacher leaders have the time to succeed.
Common Pitfalls
The work we do as educators is difficult. Leaders often find themselves constrained with limited budgets and capacity to drive change; while teachers often wish for another hour in the day to make that additional phone call home or photocopy for the next day.
In launching a teacher leadership program or opportunity, look for, and avoid the following common pitfalls:
- Temporary: Teachers notice when positions are tenuous. Avoid funding sources that may not persist long enough to influence recruitment and retention.
- Detached: Roles that prevent teacher-leaders from spending a portion of their time teaching students make it much harder for them to keep teaching skills fresh and stay connected to student needs.
- Low reach: Many teacher-leadership roles actually reduce the number of students for whom the best teachers are responsible. If fewer students benefit from the best teachers, fewer will make the learning gains these teachers induce.
- Short on time: Too many teacher-leader roles are heaped on top of teachers’ other responsibilities. Co-planning, modeling, co-teaching, coaching, and collaboratively adjusting instruction based on student data require more planning time.
- Low or no pay: Most teacher-leader roles are low- or no-pay roles; this sends the message that teacher leadership is expendable, rather than essential to schoolwide success.
- Low authority, low accountability: Teacher-leaders’ formal authority and evaluations rarely align with responsibility for wider student spans and a positive impact on peer and students success.
How has has teacher leadership made in impact in your school or career? What led to success? What should be avoided? Sound off in the comments!
Sources:
- York-Barr, J. and Duke, K. “What do we know about teacher leadership”. Review of Educational Research. (2004)
- Karen Seashore Louis, Kenneth Leithwood, Kyla L. Wahlstrom, and Stephen E. Anderson, “Investigating the Links to Improved Student Learning,” University of Minnesota (2010).
- Louis, Leithwood, Wahlstrom, and Anderson, “Investigating the Links to Improved Student Learning”
- Leading Educators and the Aspen Institute, “Teacher Leadership that Works,” Aspen Institute (2014).
- C. Kirabo Jackson and Elias Bruegmann, “Teaching students and teaching each other: The importance of peer learning for teachers,” National Bureau of Economic Research No. 15202 (2009);
- Cory Koedel, “An empirical analysis of teacher spillover effects in secondary school,” Economics of Education Review, Vol. 28, 682–692 (2009);
- Kun Yuan, “A value-added study of teacher spillover effects across four core subjects in middle schools,” Education Policy Analysis Archives, Vol. 23, no 7 (2015).
Teacher Leadership: More than a Buzzword
The education field loves jargon. From “21st-century learning” to “college and career readiness”, new jargon enters our vocabulary as priorities and policies shift. Recently, we’ve heard one buzzword repeatedly swirling across blogs and conferences: Teacher Leadership.
What is teacher leadership?
In What do we know about teacher leadership?, Jennifer York-Barr and Karen Duke from the University of Minnesota reviewed two decades of literature and define teacher leadership as “the process by which teachers, individually or collectively, influence their colleagues, principals, and other members of the school community to improve teaching and learning practices with the aim of increased student learning and achievement”
A few key ideas about teacher leadership stand out:
- It is a process, not just a position. Anyone, at any level of an organization, can demonstrate leadership. Formal roles can be helpful, but are not the end goal.
- It is about influence beyond the self—whether that be on peers, managers, subordinates, etc.
- It is ultimately about increased student learning and achievement.
Why teacher leadership?
Leading Educators put it best: “When administrators and teachers share leadership, teachers’ working relationships are stronger, student achievement is higher, and highly effective teachers can be retained in the schools that need them. Highly effective teachers can have substantial spillover effects on their peers’ performance.”

Much like a lesson or unit plan, teams should start with the end in mind: identify the specific rationale behind investments in opportunities for teacher leadership. School systems may pursue teacher leadership to:
- Further develop top teacher talent
- Help other teachers improve
- More effectively implement key priorities (e.g., curricula, standards)
- Build a pipeline to the principalship
- Distribute leadership within schools and make principals’ span of supervision manageable
- Increase highly effective teachers’ impact on student learning
- Increase teacher retention by investing in them and their ideas
Once a school, district, or network identifies why they want to invest in teacher leadership–including specific measurable goals–it becomes critical to design initiatives that will maximize that investment.
Intrigued? In our next post, we will share best practices for successfully launching teacher leadership initiatives. Hungry for more? Check out The Network Effect from Chiefs for Change and Public Impact’s Opportunity Culture.
Put Excellence at the Heart of Performance Management
Performance management, at its core, sets expectations. It puts a stake in the ground for what “good” looks and sounds like in the classroom and serves as the baseline of teacher observation rubrics. Effective performance management is more than diagnosing current performance; it supports teachers to articulate an actionable, clear trajectory toward excellence. Ultimately, a vision of good teaching and learning must be at the heart of any performance management system.
Common Pitfall: Framework Without Vision
Too often schools and districts launch a performance management system by creating or selecting a rubric without consideration of core instructional priorities. Enthusiasm and urgency, while helpful, can lead to less than ideal system design.
For example, simply adopting an existing framework because it is “proven” or “research-based” might not actually lead schools and teachers to excellence: what might be excellent teaching in one context might not be true in another setting. Creating a framework from scratch in a vacuum, separate from instructional priorities, isn’t likely to lead teachers to excellence either.
This doesn’t mean that adopting an existing framework is the wrong strategy, or that creating something new won’t get leaders and teachers where they need to be. It does mean, though, that this work must be grounded in the core realities of instruction necessary to move kids.
Ground Performance Management in a Vision for Excellent Instruction
Co-design and co-own by instructional leaders. Defining excellence for as complex a role as teaching requires a team of individuals, with different areas of expertise and focus. While very often, the development of teacher evaluation systems lives within talent/human resources, great systems strategically draw in additional stakeholders. For quality operations, a talent leader should drive and own the design and implementation of a performance management framework. At the same time, this work should be a shared priority between leaders of talent, academics and school management functions in a network or district. Instructional leaders working in schools daily must be the core authors and implementers of expectations for teachers.
Measure what matters. If teachers are held to expectations through a framework that aligns with core instructional priorities, schools are more likely to see improvement in the areas that matter most for students. If a solid instructional vision grounds all decision making, then curricular resources, training, and other supports will naturally stem from that vision. As teachers are supported to meet expectations via appropriate the resources, materials, and training, student learning will flourish.
Lead from your vision. Consider the following questions, and strategically engage others to ensure answers reflect the perspectives of a broad range of stakeholders:
- What are our prevailing beliefs within our system about students, and the role teachers play in their success?
- What do the instructional standards require from our students? And then, by extension, from our teachers?
- In classrooms where good teaching and learning is happening, what are teachers doing? What are students doing?
- How does this differ for different students? Different contexts?
- How do we ensure that the performance management system we design reflects our vision of excellent teaching?
- Who will own this work? How will we ensure that leaders from talent and instruction both continue to be involved?
Let us know what you think in the comments below!
-Jessica
Designing Evaluation Frameworks with Development at the Core – Part III: Amplifying Stakeholder Voice with Surveys
This post is the third in a series on how innovators are reimagining the design and implementation of evaluation and development frameworks. Read our earlier posts on observation frequency and raising rubric rigor.
When you think of a teacher, where are they? What are they doing? If you envisioned someone standing in front of a blackboard, lecturing a group of students, you’re likely not alone. In reality however, teachers spend their days in a multitude of ways: working individually with students, collaborating with peers, planning independently, connecting with parents and family members.
Definitions of excellent teaching therefore must go beyond classroom observations and measures of student outcomes (both of which are important!), to gather a broader view of a teacher’s impact.
Surveys are a simple, yet powerful tool that can amplify the voices of stakeholders from across a school community to help educators develop a comprehensive view of excellence.
The Benefits of Administering Surveys
- Surveys, coupled with other measures like classroom observations, provide rich information to help teachers improve their practice. Teaching is a complex job that depends on strong relationships. While districts and schools have made progress in collecting data and providing feedback on certain aspects of the profession (e.g., content knowledge, teaching strategies, assessment data), our field often misses the opportunity to coach teachers on their relationship building with students, families and peers.
- Research says that students are reliable evaluators of a teacher’s impact. Analysis by the Measures of Effective Teaching (MET) project finds that teachers’ student survey results are predictive of student achievement gains. In other words, students know an effective classroom when they experience one.
- Surveys provide the opportunity to put values into practice. Value statements like “we are a team and family” or “parents are partners” are powerful; however, these beliefs are only as true as the actions taken to build an authentic community. Administering surveys of key stakeholders sends a strong message that the voices of community members are valued, respected and heard.
- Surveys provide clear and transparent expectations to teachers. When questions are shared with teachers in advance, the survey content provides clear definitions for expected behaviors in teacher-to-teacher, teacher-to-student, and teacher-to-family relationships. For example, if a survey asks families if they receive one or more positive phone calls a month from their child’s teacher, that sets a very clear expectations for the teacher-family relationship.
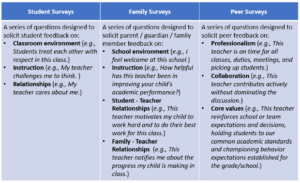
Survey Types
Educators have available a number of survey types, structures, question formats and administration platforms.The table below highlights three common survey types.
Surveys should be designed thoughtfully, taking into consideration the purpose, audience, and respondents.
- Purpose – Why are you administering the survey? What do you hope to learn? How will results be utilized?
- Audience – Who will analyze and interpret the survey results? When and how will they reflect on and plan from the results? How will the results be debriefed with teachers to improve practice?
- Respondents – Who will complete the survey? When and how will they complete the survey? What directions, supports and technology will be necessary for administration?
To learn more, including a list of sample survey questions, visit the resources page of our website.
Designing Evaluation Frameworks with Development at the Core – Part II: Raising Rubric Rigor
This post is the second in a series on how innovators are reimagining the design and implementation of evaluation and development frameworks. To read our first post in the series, on the impact of frequent observations, click here.

Most teacher evaluation systems today include direct observations of teacher practice by an administrator, in which the administrator determines ratings by assessing what they observed against a common performance rubric. It is challenging to capture the complexity of teaching in a single document, however strong rubrics have the capacity to set clear expectations, establish a common language, and chart a course for development over time.
During our work with school systems across the country, we have seen a few common challenges with widely-used rubrics:
1. Structure: Rubrics can be too long, wordy, and easy to master.
When rubrics are too lengthy, they can be overwhelming or intimidating to educators, fail to prioritize high-leverage teacher actions over lower-impact strategies, take too long for observers to complete and are challenging to norm across multiple raters. Additionally, when rubrics are too “easy”–that is when basic instruction with minimal impact on student learning aligns to language at the highest levels–we rob educators of a true pathway for growth in their careers and limit their potential for excellence.
2. Framing: Rubrics generally focus only on teachers.
When rubrics describe only what teachers are doing and saying they fail to take into account what matters most: the impact of instruction on students. This can limit the value of observation feedback and lead to misalignment between observation ratings and other components of an evaluation framework.
3. Content: Rubrics are often not aligned to today’s raised academic expectations.
When rubrics do not call for rigorous instruction aligned to core content standards (Common Core, Next Generation Science, etc.) they miss the opportunity to set expectations for learning at the appropriate bar. Similarly, as our knowledge of social-emotional learning, cultural competency, and technology expand, many rubrics have yet to adapt and account for new knowledge and skills.
In the face of these challenges, innovators are creating a new normal for observation rubrics. Through our partnership with school systems across the country, we have seen that there is no one right way or perfect rubric. Rather, systems need to consider their unique culture, expectations, observer skill level and existing structures to find or develop a rubric that will work best for them.
DREAM Charter School: DREAM prioritized finding a streamlined observation rubric that would be appropriately rigorous as teacher advances along their career while less cumbersome than the tool they had previously been using. Following research into available tools and piloting of a select few, DREAM identified the TNTP Core Teaching Rubric as the right resource: it was aligned to academic content standards, written in the form of student outcomes, and best of all, was only four pages long! DREAM revised some language to incorporate school-specific competencies that drive their unique student and adult culture. Following the first year of implementation, nearly 80% of teachers said the rubric defines excellent instruction well.
KIPP Houston Public Schools: The original and largest KIPP region is currently piloting the Reach to Rigor rubric, a new tool created in-house that defines academic and cultural expectations for teachers and students. The rubric is broken down into four parts with only the most critical components of great instruction included. The rubric language also includes both teacher and student actions, to ensure that instructional moves by the teacher are only deemed high-quality if they have the desired effect on student thinking and behavior.
Achievement First: One of the first movers in formalizing a career pathway for teachers, Achievement First has refined their approach to observation and feedback over time. The network developed and launched an updated AF Essentials Rubric that was intentionally designed to be concise, clear, focused on student actions. The rubric is aligned to the Common Core and expectations of Advanced Placement courses, shifting more emphasis to intellectual rigor and deep student thinking. The rubric includes both “foundational” (e.g., tight classroom or kids on task) and excellence (e.g., investment and deep student thinking) criteria.
What are other innovations in observation rubrics? Add your ideas and/or experiences in the comments section below.
5 Strategies for Scaling Effective Coaching
Our team spends a lot of time thinking about how to develop teachers. We believe that investing in the professional growth of teachers has the potential to dramatically change the landscape of education in our country and the lives of millions of children. While school systems across the U.S. spend billions of dollars annually on teacher professional learning and development we have little proof of their efficacy (The Mirage, TNTP 2015).
Given this context, we were thrilled to read a new study, The Effect of Teacher Coaching on Instruction and Achievement by Matthew Kraft and Dylan Hogan of Brown University and David Blazar from Harvard University. Kraft and his team conducted a meta-analysis of 37 studies and found coaching programs to positively impact instruction (.57 standard deviations) and student achievement (.11 standard deviations). The authors offer the following summary:
The results of our meta-analysis suggest that teacher coaching programs hold real promise for improving teachers’ instructional practice and, in turn, students’ academic achievement. These findings provide strong motivation to invest in efforts to scale up teacher coaching models, and to expand and improve upon the existing research base.
Effective Coaching
The authors characterize the coaching process as one where instructional experts work with teachers to discuss classroom practice in a way that is:
- Individualized: one-on-one sessions
- Intensive: frequent interaction between teachers and coaches (e.g., at least every couple of weeks)
- Sustained: coaching support over an extended period of time
- Context-specific: coaching on their practices within the context of a teacher’s classroom
- Focused: teachers and coaches engage in deliberate practice of specific skills
These findings support much of the work we have done with school systems including KIPP Austin Public Schools, DREAM Charter School and the Cleveland Metropolitan School District to grow talent through multiple-measure evaluation and development frameworks. Each of these organizations have employed innovations specific to their unique contexts, however common across all approaches is a theory of change that recognizes the critical role coaches play in moving teacher practice and ultimately student outcomes.
Scaling Systems of Effective Coaching
One of the most important insights in the analysis is data suggesting “that coaching can have an impact at scale” but that scaling-up programs (to more than 100 teachers) is challenging, particularly in building a cohort of capable coaches and in establishing strong teacher buy-in.
From our experience, these two factors matter mightily. There are certainly pockets of excellent coaching in every school system, but the real challenge of scale is consistency of implementation. Here are five strategies for solving the scale-up challenges described by Kraft, Blazar and Hogan:
1. Establish a common definition of excellence: Coaching is incredibly hard work as it requires deep content knowledge, pedagogical expertise, emotional intelligence and strong interpersonal communication skills. One the best steps we can take to set coaches up for success is adoption of a clear definition of excellent teaching (e.g., a robust rubric or vision of excellence document). In establishing a common bar of quality of important instructional practices and a common language, coaches and teachers have a clear development road-map to work along. You can read more about strong observation rubrics in this March 2017 post.
2. Make Tools Available: Great coaches need tools to guide their learning and development. School systems should develop and train leaders on a common observation debrief protocol or conversation guide such as Paul Bambrick’s 6-Steps to Effective Feedback or the TEF Debrief Planning Guide to structure coaching conversations. Systems for capturing, analyzing and sharing observation data including observation ratings and feedback are also vital for supporting coaching efforts.
3. Invest in ongoing leader development: Often lost in conversations around teacher professional development is the importance of ensuring professional learning for those responsible for coaching teachers. These professionals warrant the same level of thoughtful support. Summer is a great time to bring coaches together for intensive training but without ongoing follow-up, development can be lost or minimized. Managers of coaches should have talent development within their core responsibilities including time for managers to observe and support school leaders/coaches working with their teachers.
4. Build a Culture of Transparency and Continuous Improvement: Ultimately the work leaders do coaching teachers is only as impactful as the level of trust and partnership teachers feel in the relationship. Transparent communication of the “why” and “how” of key policies along with timelines, goals, and progress to-date is essential for successful long-term investment. Gathering frequent feedback with public recognition of the findings and appropriate next steps will build a culture of continuous improvement.
5. Phase-in implementation: As noted in the study, working one-on-one with any person over a sustained period requires an investment of time and money. Certainly shifting funds from less effective professional development activities toward coaching is a strong first step. Another strategy is to phase-in implementation of a coaching program to build capacity, gain early wins, expand the coalition of supporters, and prove the value of the financial investment. We suggest system leaders identify the core problem they are hoping to solve, then target the first phase of implementation toward that issue. For example, if a system seeks to solve the challenges that arise from new teachers lacking foundational classroom management skills they can launch a coaching program focusing on that subset of teachers. Over time, coaches could roll-off and target other groups of teachers for support or the program could expand with the hiring of additional coaches.
What approaches to coaching teachers have you seen work well? How have you built a cohort of strong coaches and/or invested teachers? Let us know in the comments below!
Great Leaders, Great Teachers: How Cleveland Metro is Investing in Leaders
In response to Race to the Top, many states, including Ohio, revised state statutes requiring school districts to develop new evaluation models. In a collaborative effort, the Cleveland Metropolitan School District and the Cleveland Teachers’ Union developed the Teacher Development and Evaluation System (TDES).
We partnered with the talent team at CMSD to develop tools and trainings designed to enhance administrators’ ability to successfully evaluate and develop their teachers. We began the engagement with a robust review of existing research and best practices in order to establish a clear description of the knowledge and skills necessary for leading effective observation and feedback.
Following stakeholder review and investment in the new district-wide expectations, we established a theory of action for building administrator capacity across the district, developing an aligned scope and sequence of training modules aimed at achieving CMSD’s goals. Each training module focuses on both observer calibration and quality feedback for improvement, sharing tools and protocols aimed at bridging the learning into the daily practice of administrators.
Taken together, these training modules provided administrators regular opportunities to reflect on and hone their practice as instructional leaders, improving teacher quality and ultimately, the achievement of students across the district.







